| images | ||
| .gitignore | ||
| esp8266-geigercounter.ino | ||
| LICENSE | ||
| README.md | ||
| settings.h.example | ||
Mightyohm.com Geigercounter connected to ESP8266
❗ This project assumes that you know how to solder, flash an arduino and use MQTT. This repository is not a tutorial - there are plenty of them around the internet. This repository serves the purpose to provide the code to anyone who wants to use it, or extend it yourself to your needs ❗
ESPHOME
This can now also be done by ESPHome, if you want to go this route.
uart:
id: uart_bus
tx_pin: D3 # D10 (TX)
rx_pin: D1 # D9 (RX)
baud_rate: 9600
sensor:
- platform: template
id: geiger_cpm
name: "Geiger CPM"
unit_of_measurement: "CPM"
accuracy_decimals: 2
filters:
- throttle_average: 60s
- platform: template
id: geiger_usv
name: "Geiger µSv/hr"
unit_of_measurement: "µSv/hr"
accuracy_decimals: 2
filters:
- throttle_average: 60s
interval:
- interval: 1s
then:
- lambda: |-
static std::string buffer;
while (id(uart_bus).available()) {
uint8_t c;
if (!id(uart_bus).read_byte(&c)) break;
if (c == '\n') {
// Process a full line
float cpm = NAN;
float usv = NAN;
std::string line = buffer;
buffer.clear();
// Example: CPS, 00123, CPM, 00456, uSv/hr, 2.53, SLOW
size_t cpm_pos = line.find("CPM,");
if (cpm_pos != std::string::npos) {
size_t cpm_end = line.find(",", cpm_pos + 4);
cpm = atof(line.substr(cpm_pos + 4, cpm_end - (cpm_pos + 4)).c_str());
}
size_t usv_pos = line.find("uSv/hr,");
if (usv_pos != std::string::npos) {
size_t usv_end = line.find(",", usv_pos + 8);
usv = atof(line.substr(usv_pos + 8, usv_end - (usv_pos + 8)).c_str());
}
id(geiger_cpm).publish_state(cpm);
id(geiger_usv).publish_state(usv);
} else {
buffer += (char)c;
}
}
getting started
To compile this code, just clone or download the master branch as a zip and ramp up your arduino IDE.
- Needed external dependencies are PubSubClient and optionally ArduinoOTA.
- Rename
settings.h.exampletosettings.h - Change the configuration in settings.h to your needs
- Select Wemos D1 Mini clone in Platform
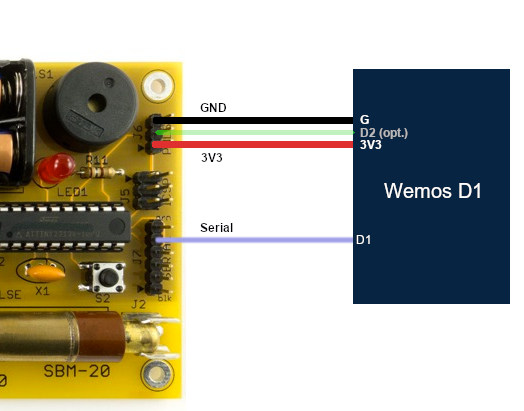
how to connect the wires
Here's some code and schematic to connect your mightyohm.com geiger counter to the Internet of Things (IoT).
You can optionally connect PULSE to D2 of the Wemos D1 and enable PIN_PULSE to receive a mqtt event each count!
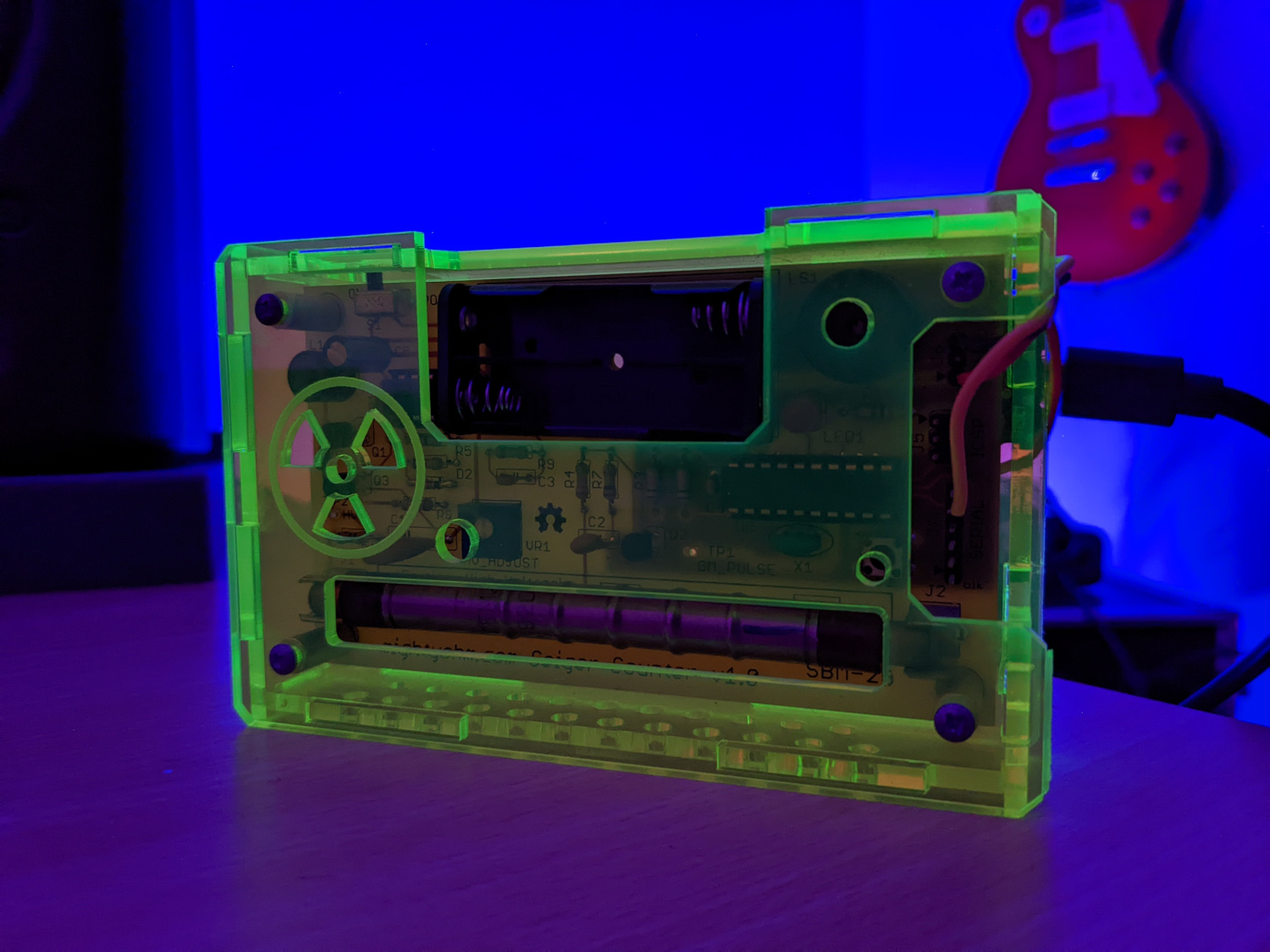
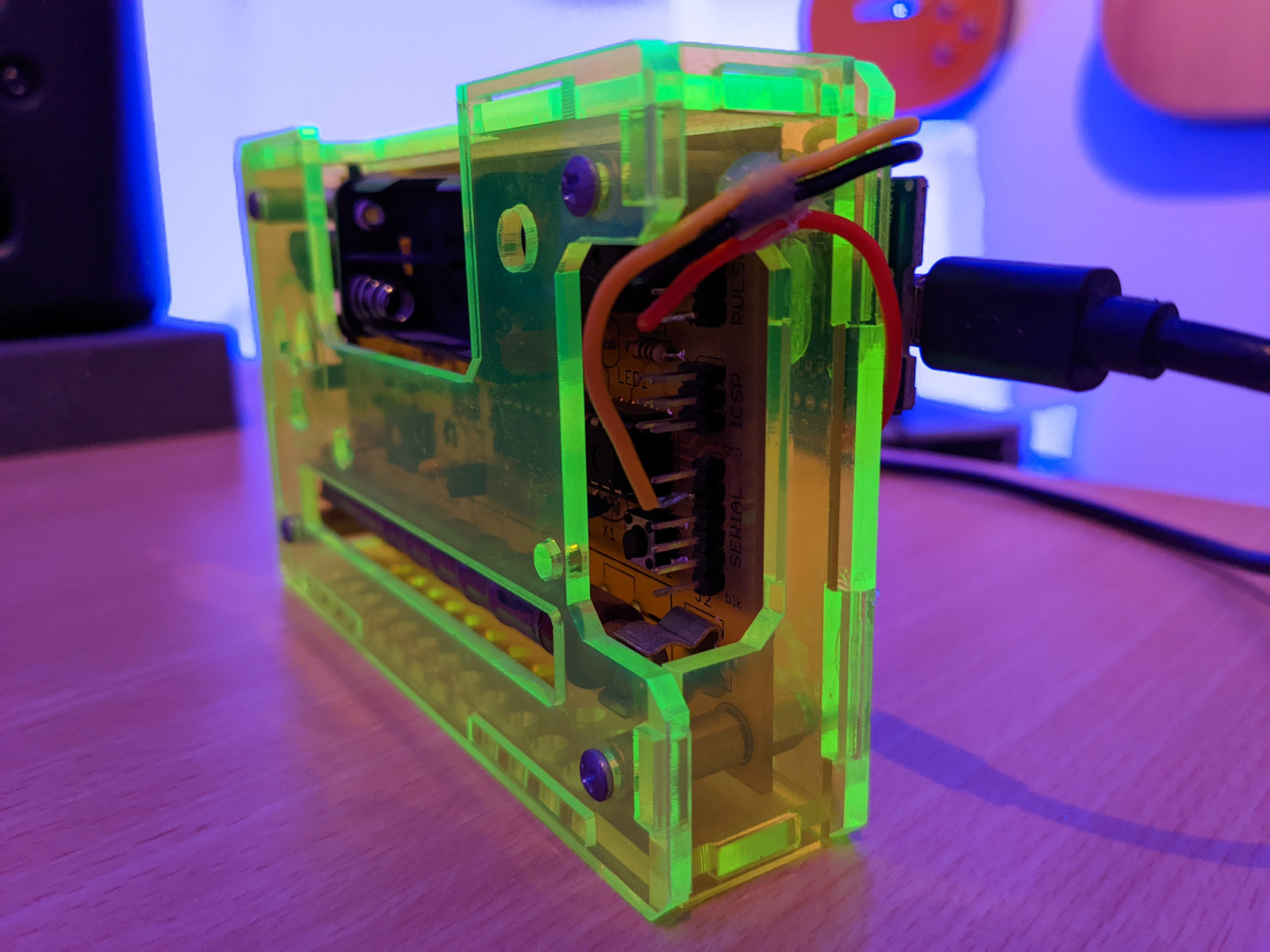
images


license and credits
This code is under MIT license (Christopher Schirner mail+github@schinken.io)